Task-Oriented Leadership: 3 Cases It Works & When to Avoid
Task-oriented leadership or task leadership is a management style that focuses on the timely completion of tasks and projects with the required quality levels. Therefore, task-oriented leaders focus on goals, objectives, and deadlines and make sure there are sufficient processes and procedures to reach the goals. Morale, motivation, and interests of the individuals are secondary for the task-oriented leadership.
In this article
Bill Gates, Jack Ma, and Tim Cook are known as the famous task-oriented leaders. In this article, we will focus on the inception and traits of task-oriented leadership, 3 cases when you should apply this leadership style, and when to avoid it.
📌 Hint: Do not skip this article, you will find FREE Leadership Training resources throughout the article.
💡 You might be interested in the 12 Great Leaders Affected Our Lives in the Last 25 Years article.
Inception of Task-Oriented Leadership
Task-oriented leadership has been used for several years and there is no credit for a particular theorist or leader regarding its foundation. There are several managerial and leadership models focusing on task leadership. The most popular ones are the situational leadership model by Hersey and Blanchard and Blake Mouton Grid.
Robert R. Blake and Jane Mouton are the founders of the Blake Mouton model. The inception of the model dates back to 1964. The original model defines leadership in five different leadership styles based on two dimensions: concern for people and concern for the production or results (or tasks). You can see the Blake and Mouton grid and five different leadership styles in the figure below.
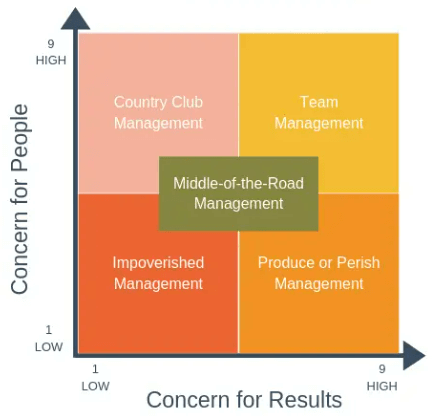
As you can see in the figure, one dimension shows the manager’s or leader’s degree of task, production, or result-centeredness and the other dimension shows the person-centeredness. Each dimension is scored from one to nine. And, depending on the scores of these two dimensions, appropriate leadership among these five types is determined.
Dimension #1 – People-Oriented Leadership
This degree of the Blake Mouton Model shows the leader’s concerns for their followers. For instance, if the leader is too interested in the needs, self-interests, and demands of individuals, such as a servant leader, the degree of concern for people will be high, e.g. nine. If the leader is just focusing on the tasks to be accomplished and does not give that much importance to people, morale and motivation, such as an autocratic leader, the degree of concern for people will be low, e.g. one.
Dimension #2 – Task-Oriented Leadership
This dimension of the Blake Mouton Model shows the degree to of a leader emphasizes concrete objectives, organizational efficiency, and high productivity when deciding how best to accomplish a task. If the leader is too worried and concerned about the production, the degree of concern for the results will be high, e.g. nine. Adversely, if the leader is not interested in the results, the degree of concern for the results will be low, e.g. one.
Based on the degree of concern for people and concern for results (tasks or production), the appropriate leadership style is determined. Considering the five different types of leadership styles, adaptive leadership skills may be required to apply Blake Mouton’s model leadership styles.
Enhance Your Leadership Skills – Executive Leadership Training Program
San Francisco Business School offers an online, self-paced comprehensive executive leadership training program. You can consider enrolling in this program to improve your leadership skills.
7 Traits of Task-Oriented Leadership
While there are several characteristics of the task-oriented leadership style, we have listed the top 7 characteristics. This leadership resembles refers to autocratic leadership and transactional leadership traits.
1- Minimum Group Participation
Great leaders value group participation, knowledge-sharing, and discussion. However, task-oriented leaders decide on their own, based on their insights and experience. They ask no questions, or minimum questions to their team members. They order the team and expect the team to follow them with little or minimum questions. The primary concern of the task-leadership is finishing tasks on time without compromising from quality.
2- Task Oriented-Leadership Focuses on Short-Term Goals
You should have heard the three famous theories about motivation: McGregor’s Theory X and Y, Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, and Herzberg’s hygiene factors. These are famous and phenomenal theories about people’s motivation. The common part of these famous theories is, that people can be motivated by material rewards to some degree. If the material compensations are below the average, this makes people demotivated, however, having generous compensation or rewards will not make people very motivated. People look for other motivational factors such as encouragement, relationships at work, self-actualization, etc.
The task-oriented leadership style focuses on short-term goals. The management tries to accomplish quick wins around a tight schedule. Therefore, instead of building relationships, encouraging team members, and growing the team, people are motivated by rewards. This resembles the Authoritarian Leadership style.
3- Clear Rewards and Penalties Policies
The backbone of the task-oriented leadership style is rewards and penalties. Leadership clarifies its expectations from the beginning with a clear set of goals and targets. Rewards and penalties policies are also declared to the team. While objectives are met, rewards are given to those who deserve them. If there are underperformers or unwanted behavior, the task-oriented leader will not hesitate to punish them.
This aspect of task leadership resembles the transactional leadership style.
4- Task-Oriented Leadership Minimizes Relationship Building
The goal of the people under task leadership is to reach goals and gain rewards. However, this might be at stake to compete against other team members in the team. In other words, the team members in the same team might be the competitors of each other. Respectively, this minimizes the development of personal connections, blocks team-building, and hinders team development.
5- Provides Leaders Dictatorship
“Dictatorship” may sound repressive. However, task-oriented leadership allows the leaders to dictate the ground rules, methods, tools, techniques, and processes to the team. This is a must to ensure quick decision-making and application.
6- Discourages Creativity and Innovation
In task-oriented leadership environments, leaders expect the team members to perform their tasks with no or minimum questions asked. There is no room for innovative thinking or creativity. Even if the resources are capable of providing creative and innovative outputs, task-oriented leadership may hinder their capacity.
7- Establishes Clear Rules and Communication
Task-oriented leaders make quick decisions and expect their team to follow them immediately. They expect quick results. This requires a clear set of rules and communication. So, team members do not hesitate on the tools or processes to use when they are performing their tasks.
Free Online Leadership Skills Training Program
One of the requirements to be a good leader is to improve yourself continuously. The best way to do this is, to enhance your competence through training. Take a step ahead and jumpstart your leadership competence. Enroll in our 1-hour Free Leadership Training program.
3 Cases to Use Task-Oriented Leadership Style
Task-oriented leadership solely focuses on the timely completion of tasks or projects. This may sound positive, however, in some cases, task-oriented leadership ignores the morale, motivation, and personal interests of the team members. Therefore, this leadership does not fit in every environment.
3 Cases to Apply Task-Oriented Leadership
Emergencies, time-critical tasks, and having an inexperienced team are the best cases to apply task leadership.
- Emergency cases: quick decisions and fast reactions are needed in case of emergencies. This requires minimum time to decide on a solution. task-oriented leadership will work in emergencies.
- Time-critical tasks: When there is time pressure, there might not be time to evaluate different perspectives and opinions from the team. Task-oriented leaders make decisions, and team members follow orders. Therefore, task leadership may be beneficial for time-sensitive projects or tasks.
- Inexperienced teams: If your team members are junior and need maximum guidance to perform, autocratic leadership may be better. Also, it is less likely to receive creative ideas from junior professionals, so, group participation may not be needed if you have an inexperienced team.
3 Cases to Avoid Task-Oriented Leadership
If you have creativity-requiring tasks, team development and training, and relationship-building tasks, avoid using a task-oriented leadership style.
- Creativity-Requiring Projects/Tasks: Creativity and innovation requires group collaboration. To ensure this, group members must be encouraged to maximum participation. This allows new ideas to arise from the team. This is against the autocratic leadership culture.
- Team Development and Training: If you are growing the competence of your team or enhancing their skills, you need to talk and get feedback from them. Therefore, you need maximum involvement of the team during team development and training.
- Relationship-building Projects/Tasks: If your work requires interaction with your team members, you need to build your relationship with each and every individual in the team. task-oriented leadership may not be appropriate in these cases.
Watch Laura’s 30 Seconds Experience – Executive Leadership Program
Hear from Our Alumni Laura Smith, Head of Design. Laura attended the Executive Leadership Program at SFBS.
Famous Task-Oriented Leaders
When we searched for the famous task-oriented leaders on Google, it showed the following results. We will be focusing on Richard Branson, Tim Cook, and Jack Ma’s task-oriented leadership styles in this article as we refer to other leaders in our other articles.
1- Richard Branson
Sir Richard Charles Nicholas Branson (born 18 July 1950) is a British business magnate and commercial astronaut. In the 1970s he founded the Virgin Group, which today controls more than 400 companies in various fields. Branson’s following quote shows his belief in task-oriented leadership.
“I believe in benevolent dictatorship provided I am the dictator.”
2- Tim Cook
Timothy Donald Cook (born November 1, 1960) is an American business executive who became the chief executive officer of Apple Inc. in 2011. Cook had previously served as the company’s chief operating officer under its co-founder Steve Jobs. Cook’s following quotes about products show his task-oriented leadership style.
“We have to make sure, at Apple, that we stay true to focus, laser focus – we know we can only do great things a few times, only on a few products.”
3- Jack Ma
Jack Ma Yun (born 10 September 1964) is a Chinese business magnate, investor and philanthropist. He is the co-founder of Alibaba Group, a multinational technology conglomerate. Ma’s following quotes about the creation of things highlight his task-oriented leadership style.
“If you’re doing business, not that simple to only buy. You have to create something. You have to create something that never exists for the future.”
Summary
Task-oriented leadership focuses on tasks, results, and production. The ultimate performance factor is the timely completion of the tasks without compromising quality. The traits of task-oriented leadership are focusing on short-term goals, minimum group participation, clear rewards and policies, and clear rules and communication.
Task-oriented leadership works best in emergency cases, if there is a tight schedule, and if the team is inexperienced. You should avoid this leadership style if you need creation and innovation, team building, and good relationships. Although several famous leaders are applying task-oriented leadership, Richard Branson, Tim Cook and Jack Ma are three examples.

